Picture a busy weekday in a city where everyone relies on the internet for work, studies, and entertainment. Students are immersed in virtual classes, adults are managing work calls while working remotely and commuters are streaming videos on the metro, all relying on an internet connection to keep them going. From smartphones to smart homes, all are seeking faster, more reliable internet for every day, but what keeps this digital show running? A dynamic duo working together takes center stage for seamless connectivity: optical fiber cables and wireless networks. This powerful combination shapes how we work, conduct business, study, and enjoy entertainment. In this blog, we dive deep into the synergies of optical fiber and wireless network technologies.
Optical fiber cables (OFC) - The backbone to seamless internet connectivity
Apart from wireless networks, high-speed internet connections backboned by increased fiberization have allowed the pace of technological advancement you witness today. We are growing increasingly dependent on fast and reliable internet connectivity. Optical fibers step in to meet the demand for fast, reliable data transmission with high speed and minimal downtime. By using pulses of light to transmit data, optical fiber cables have revolutionized the way we communicate. They offer a level of futureproofing that makes almost all traditional copper cables obsolete. This innovative technology boosts speed and also allows huge volumes of data transmission across long distances with minimum signal degradation. Given their low latency, optical fiber cables are a necessary part of high bandwidth 5G network deployments for both home and business broadband internet.
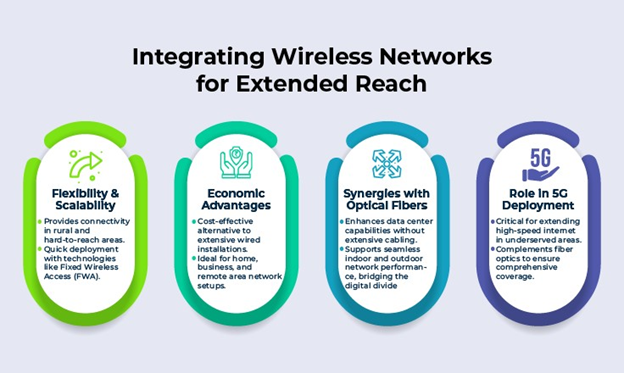
Wireless networks
While optical fiber networks have traditionally served as a strong foundation for global communication systems and have been considered the premier option for direct high-speed internet access, incorporating wireless technology into these networks is becoming increasingly sensible. Networks like Wi-Fi, cellular networks, and other wireless technologies provide flexibility for our gadget-centric lives. These networks use radio frequencies to connect devices to network nodes and are thus popular, easy-to-deploy solutions for home and business. Given the logistical challenges of laying optical fiber cables in rural, more far-to-reach areas, wireless networks offer an efficient alternative for broadband deployment. While wireless networks may not match the bandwidth of an FTTx connection, they frequently present a more cost-effective solution for subscriber connectivity compared to traditional wired optical fiber cables. Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) represents a recent 5G application, providing wireless connectivity in areas where deploying FTTx is challenging, thereby aiding telcos in capitalizing on their 5G investments.
Synergies of optical fiber and wireless networks
It's crucial to understand that wireless networks are only wireless between the antenna and each connected device. Each antenna requires support from wires for both power and data transmission, and the data itself travels over optical fiber cables. In the collaboration between optical fibers and wireless networks, optical fiber cables form the backbone, linking urban city hubs and hyperscale data centers. Optical fiber cables play a crucial role in delivering high-bandwidth data from network backbones to wireless antennas, either in proximity or directly. In older technologies like 3G mobile, fiber cables were linked to the "huts" at the base of antenna towers. However, with modern high-speed mobile networks such as 4G LTE and 5G, optical fiber cables run directly up the towers to the antennas. This direct fiber connection enables wireless networks to efficiently expand and serve mobile customers, homes, and businesses with fast and reliable connectivity. The transformative applications of integrating optical fibers with wireless networks have been particularly evident in 5G. The benefits of this integration include:
Enhanced connectivity and bridging the digital divide:
According to Statista, global internet users are forecasted to reach a new peak of 7.3 billion users in 2029. However, IAMAI and Kantar have reported that internet penetration in rural India is only 37%, even though there are 692 million active internet users in the country. This reinforces the need for a denser digital infrastructure that can enable increased high-speed broadband by combining the speed and reliability of optical fiber cables with the flexibility and convenience of wireless networks. While the Indian government is also recognizing the need for improved rural internet service with initiatives like the BharatNet project, integration of wired and wireless networks will benefit rural customers with slow or non-existent wired connections. This will significantly improve connectivity and network performance both indoors and outdoors in areas where deploying physical fiber cables is difficult. A secure and reliable wired and wireless network, in which antennas are fed by fiber cables, can have a huge impact on narrowing the digital divide given its economic advantage.-
Unveiling the factors behind quantum growth:
India is fast emerging as a data center hub owing to enormous data consumption and unique digital infrastructures like Aadhaar, UPI, and ONDC. In 2023, a CII-Colliers report ‘India Data Centers: Entering Quantum Growth Phase’ estimated that India’s data center industry will double in size to 2.14 million m2 and attract potential investment of $10 billion within the next three years. This data center growth can be attributed to businesses migrating to the cloud, with various sectors such as BFSI, manufacturing, e-commerce, and retail that are driving enormous data demand. While there is an increasing thrust on fiberization to meet evolving demands within data centers, the integration of wireless technology solutions, especially with the advent of 5G, will play a critical role in enabling data centers to efficiently deliver services to end users. By combining the high-speed and reliable backbone of optical fiber cables with the flexibility and mobility of wireless networks, hyperscalers can rapidly serve maximum number of end users, providing a cost-effective network infrastructure.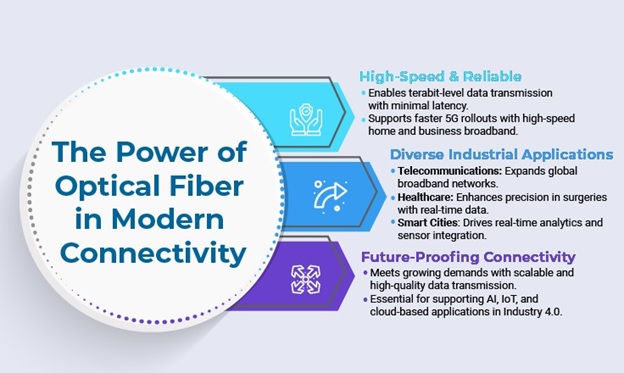
Unlocking Industry 4.0:
The world is on an upward digital trajectory that cuts across industries and enterprises. Companies are moving IT operations to the cloud and embracing new-age technologies like AI/ML, robotics, and Industrial IoT to automate processes and create smart factories that are more efficient and productive. These hyper-connected ecosystems rely heavily on high-speed, reliable network connectivity with minimal or no internet disconnections. Findings from the Information Technology Intelligence Consulting 2021 survey show that a single hour of internet downtime costs 44% of enterprises at least US$ 1 million. These changes make it even more crucial to invest in a future-proof digital infrastructure. Optical fiber cables are an excellent solution for consistent broadband connection, given their resistance to electromagnetic interference and high durability. However, the incorporation of wireless technology for the last link in an industrial or commercial network will enhance interconnection capabilities by connecting all sensors, machines, and devices to allow seamless communication and collaboration. Wireless networks can provide a fast, efficient, and cost-effective solution for high-speed internet connectivity in areas that lack a wired infrastructure.
Scaling integration for seamless connectivity solutions
To keep up with the demand for increased connectivity and to cater to emerging technologies such as satellite-based internet, wireless networks will have to increasingly interconnect with optical fiber cable networks. This integration will not merely promise high internet speed but create a connected ecosystem for users irrespective of their location. The combined strengths of optical fiber cables and wireless networks will lay a strong foundation for connectivity solutions where internet speed, reliability, and flexibility will converge seamlessly. As technology continues to advance and data consumption increases, the synergy between optical fiber and wireless networks will play a crucial role in providing fast, reliable, and cost-effective connectivity solutions for people and businesses worldwide.