As we dive headfirst into the digital age, it's clear that things are ramping up quickly. GSMA Intelligence tells us we're on track to hit over two billion 5G connections globally by 2025. That's huge! Mobile operators are all in on 5G, and it's not just about faster internet on our phones. We're talking about a game-changer for areas that have been lagging in broadband speeds. 5G is set to make things like the Internet of Things (IoT) and all those smart devices we love work seamlessly. With the advent of 5G, industry executives unanimously agree that fiber penetration must increase significantly to fully harness the benefits of 5G services. A robust optical fiber network is pivotal for 5G as it facilitates optimal network capacity utilization and the seamless transmission of large data volumes.
According to a recent report from ET, there's been a remarkable surge in the installation of optical fiber across India, growing six times since the introduction of 5G services in October of the previous year. The current monthly average of optical fiber laying has reached an impressive 101,550 kilometers. This figure is in sharp contrast to the pre-5G rollout rate, where only 16,712 kilometers were laid each month. Without any doubt, the excitement is building for the 5G broadband revolution! It's poised to be a game-changer, and we're all eagerly anticipating the ways it will enhance our daily lives.
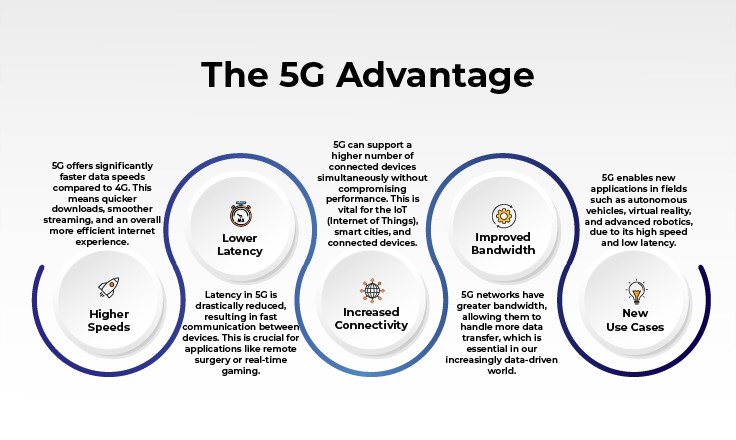
Why 5G?
5G isn't just a step up from 4G; it's a significant leap forward, opening doors to technological advancements and applications that were previously impossible. And now with the support of an optical fiber network, 5G is all set to transform the digital landscape.
How does the optical fiber network contribute to 5G connectivity?
In the fast-paced world of 5G , optical fiber network plays a pivotal role in meeting the stringent requirements and ambitious goals of this next-gen technology. Developing a strong fiber infrastructure is a fundamental part of communication. Building 4G and 5G networks requires a robust fiber backhaul. 5G networks rely on a denser network of smaller cell towers, as opposed to the larger macro cell towers of 4G, necessitating high-speed backhaul connections to the core network over long distances. With small cells becoming crucial in the 5G rollout, having a fiberized backhaul becomes extremely important.
High bandwidth and reduced latency:
Fiber optic cables are renowned for their ability to transmit data at lightning speeds. Unlike their copper counterparts, fiber cables can support the significantly higher data rates required by 5G, which are expected to be up to 100 times faster than 4G networks. This speed is vital for handling the enormous data demands of a 5G network, which is designed to connect countless devices and support data-intensive applications.
Recent Developments:
Advances in fiber optic technology continue to push the envelope, with companies now exploring 40-Gbit/sec and 100-Gbit/sec speeds. Such advancements are not just theoretical but are being implemented across various regions.
Essential for Low-Latency Applications:
The promise of 5G is not just in its speed but also in its remarkably low latency. Optical fiber cables are crucial in achieving this, offering minimal delay in data transmission. This is particularly important for applications such as autonomous vehicles, telemedicine, and augmented reality, where even a millisecond delay can be detrimental.
Technical Advantages of Fiber:
Fiber optics The promise of 5G is not just in its speed but also in its remarkably low latency. Optical fiber cables are crucial in achieving this, offering minimal delay in data transmission. This is particularly important for applications such as autonomous vehicles, telemedicine, and augmented reality, where even a millisecond delay can be detrimental.
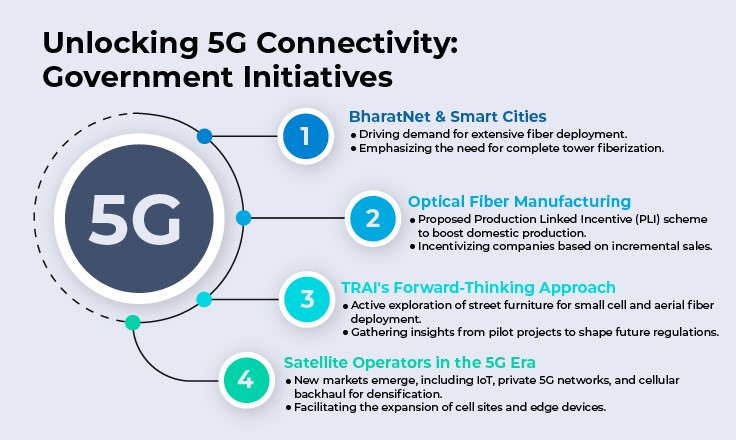
Expanding Coverage:
The push for wider 5G coverage necessitates an extensive optical fiber network. For example, the Indian government aims for a 70% tower fiberization by 2024-25 to meet the coverage demands of 5G (Source- Communications Today). This initiative reflects a global trend towards enhancing fiber infrastructure to support the vast and varied requirements of 5G networks.
Real-World Reliability:
In addition to technical prowess, fiber optic cables are immune to corrosion and can withstand harsh environmental conditions. It is even feasible to deploy subsea connections between continents to facilitate high-speed data transfer over vast distances. This real-world reliability ensures consistent data transmission, a crucial factor for the success of 5G networks.
Conclusion
According to data from Omdia, after adding nearly half a billion connections in 2022, the momentum in 5G uptake continues into 2023, with enterprise subscriptions and industrial deployments driving the surge. Global 5G wireless connections witnessed a staggering 76% increase from the end of 2021 to the end of 2022, soaring to 1.05 billion, and projections indicate it will reach an impressive 5.9 billion by the end of 2027. 5G is growing remarkably and scaling faster than any other previous generation of mobile wireless.
However, rolling out 5G is a bit like a high-tech hurdles race. In some areas, 5G deployment faces obstacles such as high infrastructure costs, device affordability, absence of a robust optical fiber network, and regulatory barriers, potentially leading to a digital divide. Despite progressive amendments to Right of Way (RoW) Rules facilitating faster telecom infrastructure deployment, on-ground implementation grapples with challenges from local entities, municipal corporations, and wards. In this dynamic landscape, overcoming these obstacles is key to realizing the full potential of 5G services.