Multimode fiber cable is a type of optical cable used for high-speed data transmission over short distances. It is widely used in local area networks, data centers, and other applications where high-bandwidth connectivity is required. In this blog post, we will discuss the key features and advantages of multimode fiber cable.
What is Multimode Fiber Cable?
Multimode fiber allows multiple modes or paths of light to travel through the fiber core.
Multimode fiber can only support transmission over short distances. At longer distances,
light traveling in different modes will interfere with each other, causing signal
degradation and bit errors. The core diameter of multimode fiber is typically larger
than that of single-mode fiber, allowing more light to be transmitted.
Multimode
fiber cables are commonly used in local area networks (LANs) ,data centers, and other
applications that require high-bandwidth transmission over short distances. It is also
used in applications such as video transmission and security systems.
Compared to
single-mode fiber cable, multimode fiber cable has a shorter maximum transmission
distance and lower maximum bandwidth. but is generally easier to install. For
short-distance applications, the overall cost of a multimode system will usually be less
than that of a single-mode transmission system.
Difference between Multimode and Single-mode fiber
Here are some key differences between multimode and single-mode fiber and cable:
-
Core Diameter:
The core diameter of multimode fiber is usually 50 microns, although 62.5 microns is found in some legacy applications. In contrast, the core diameter of single-mode fiber is usually 9 microns. Distance:
Single-mode fiber cable can transmit data over much longer distances than multimode fiber cable. Multimode fiber cable is generally used for distances of less than 300m and can support transmission up to 2 km at relatively low data transmission rates. Single-mode fiber can transmit data over distances of up to 40 km or more, with very high transmission rates possible when wavelength-division multiplexing is used.Light Source:
Multimode fiber cable is typically used with low-cost LED or VCSEL (vertical cavity surface-emitting laser) light sources, while single-mode fiber cable is exclusively used with laser light sources.Cost:
Due to the relative cost of the light sources, for short-distance applications, multimode fiber cable systems are generally less expensive than single-mode fiber cable systems.Applications:
Multimode fiber cable is commonly used in LANs, data centers, and CCTV systems, where the overall cost of a multimode system is less than that of singlemode. Single-mode fiber cable is typically used for long-distance applications, such as telecommunication networks and cable TV systems, with transmission distances beyond the range of multimode fiber.
How Do Multimode Fiber Work?
Multimode fiber works by using multiple paths or modes to transmit light signals over
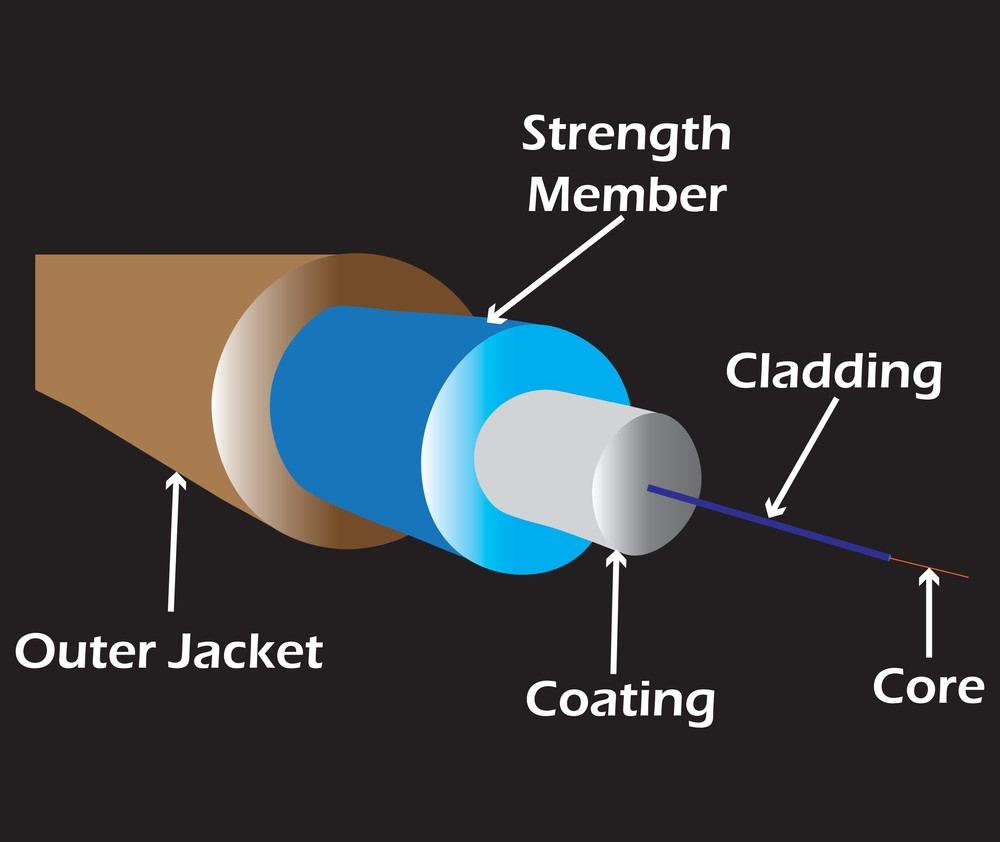
short distances. The fiber consists of a core, which is the central part of the
cable where the light travels, a cladding layer, which surrounds the core and helps
to keep the light confined within the core, and a coating to cushion and protect the
fiber.
When light is transmitted through a multimode fiber, it enters the core at
one end of the cable and is reflected off the walls of the core at different angles.
These multiple angles cause the light to take multiple paths, or modes, through the
core, hence the name "multimode" fiber. The light signals are transmitted over these
multiple modes simultaneously, allowing for multiple signals to be transmitted at
the same time.
However, because the light takes multiple paths through the core,
the signals tend to degrade as they travel farther down the fiber. This is known as
modal dispersion, and it limits the range of multimode fiber compared to single-mode
fiber.
To compensate for this degradation, multimode fibers are typically
designed with a larger core diameter, which allows for more modes to be transmitted
at the same time, increasing the bandwidth of the cable. Additionally, multimode
fiber cables may be used with specialized transceivers or other equipment that can
help reduce modal dispersion and increase the range of the cable.
Multimode
fibers are commonly used in LANs, data centers, and campus applications where the
cables containing and protecting the fiber are completely or partially run within
buildings. As a result, multimode fiber cables are often flame-retardant to protect
human life and safety.
Conclusion
Multimode fiber cable is an excellent cost-effective choice for high-speed data transmission in a variety of applications where the transmission distance is relatively short. Its ability to carry multiple modes of light launched by low-cost LED and VCSEL sources allows for fast and efficient data transfer. With its relatively low system cost and easy installation and maintenance, it's no wonder that multimode fiber cable is a popular choice for many businesses and organizations.