The global microduct market, with a valuation of USD 4.06 billion in 2021, is on an upward trajectory. Projections indicate a growth from USD 4.41 billion in 2022 to a substantial USD 9.08 billion by 2029, demonstrating a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 10.8% throughout the forecast period. Microduct cabling solutions represent a major advancement in cable installation within ducts or conduits, utilizing blowing technology. This method has gained global prominence as the preferred technique in modern times. Serving as a protective sheath, similar to a tube, microducts house microcables or microduct optical fiber cables. These components are essential in creating a comprehensive and organized data network, facilitating the expansion of fiber network infrastructure. However, to build such an infrastructure the right cable selection is crucial.
As the demand for high-speed and reliable data transmission continues to grow, the right cable selection becomes paramount. Microduct cables play a crucial role in facilitating the seamless flow of information through fiber optic networks. To ensure optimal performance and longevity, it's essential to consider various cable parameters before making the right cable selection.
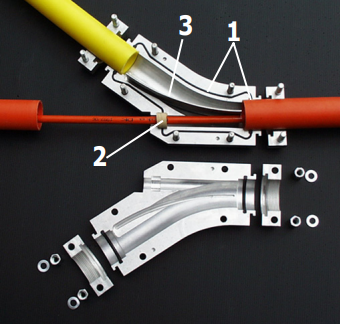
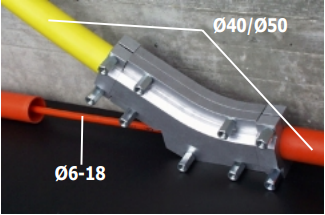
Figure: Y-connector (Image Courtesy: Plumettaz SA)
The benefits of Microduct Blowing are outlined as follows:
- With advancements in cable and duct design, blowing distances have significantly increased.
- The use of continuous lubrication systems, which apply a thin lubricant film during blowing, reduces friction between the cable's outer surface and the duct's inner surface.
- Microduct Cabling simplifies the process of branching cables.
- Y-connectors allow for cable overlay in ducts that are already occupied by previously installed cables, leading to considerable cost savings during cable route upgrades without the need for excavation.
- Additional, smaller microducts can be blown into the remaining space in standard ducts, creating new pathways for additional cables.
- The deployment of networks is faster and more efficient, offering a better return on investment due to the reduced need for machinery.
- Fewer method installation crew members are required.
- This is safer for fiber optic cables as it applies less stress than other techniques.
- Old ducts can be repurposed for route upgrades.
- Maintenance and cable replacements can be completed quickly in the event of damage.
Factors to consider before choosing the best microduct cable for your specific needs:
1. Selecting the Right Duct:
Choosing the appropriate duct is a critical aspect of cable installation, and maintaining the right cable-duct ratio is imperative. Ideally, the Cable Outer Diameter (OD) to Duct Inner Diameter (ID) ratio should fall within the range of 0.6 to 0.7. This optimal ratio ensures proper fit and reduces the risk of issues such as cable damage or inefficient use of the duct space. Moreover, the inner wall of the duct plays a pivotal role in ensuring smooth cable installation. A polished duct inner wall is essential to reduce the friction coefficient during the cable-laying process. Different types of duct interiors are available, including smooth inner walls with low-friction liners, straight ribs, and grooved surfaces. It's important to ensure low friction between the duct's inner wall and the cable's outer jacket to achieve longer blowing distances. Therefore, attention to the duct's inner wall condition is a key factor in enhancing the reliability and performance of the cable infrastructure. Additionally, consider the microduct configuration – whether it's a single-duct or multi-duct system – based on the number of cables you plan to install and the network's scalability.
2. Fiber Count and Density:
One of the primary considerations when doing an optical fiber cable selection is the fiber count, which refers to the number of individual fibers within the cable. Assessing your current and future bandwidth requirements is crucial in determining the appropriate fiber count. Additionally, consider the cable's density – how closely the fibers are packed within the microduct. Opt for a cable that strikes the right balance between fiber count and density to meet your network's capacity needs.
3. Cable Construction:
The construction of the cable plays a vital role in its performance and durability. Different applications may require specific types of cables. Evaluate your environmental conditions and installation requirements to choose the right cable construction.
- The microduct cable needs to be optimally stiff, enabling it to cover longer distances in a single installation effort.
- The stiffness of the cable should correspond to the characteristics of the duct route.
- In routes with numerous straight sections, a stiffer cable is more effective.
- For routes with many bends, a more flexible cable is preferable.
It's important to factor in the length of the cable since it influences the duration of the installation. Make sure that the cable's outer diameter is compatible with the inner diameter of the microduct, taking into account the duct fill ratio. Ideally, this ratio should be between 60 – 70%; above 85% is considered high, while below 45% is low. Due to their smaller diameter, micro cables typically exhibit lower mechanical properties compared to the larger, conventional cables.
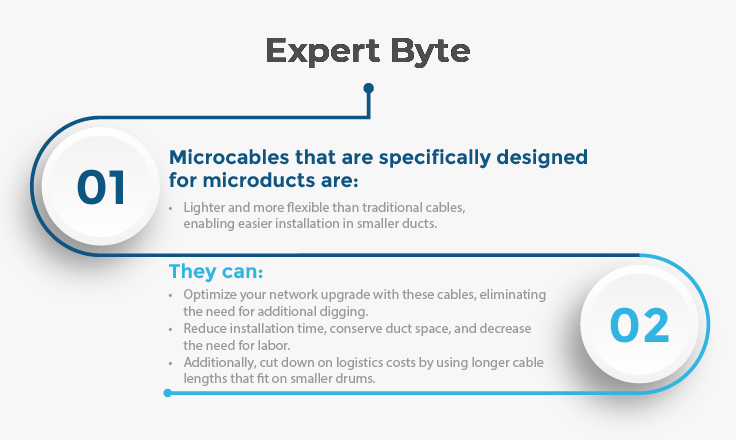
4. Bend Radius and Installation Considerations:
Microduct cables may undergo bending during installation, and their ability to handle such bending is crucial for performance and longevity. Evaluate the cable's bend radius – the minimum radius a cable can bend without compromising its optical performance. Ensure that the selected microduct cable can meet the installation requirements, including any specific bending radii, pulling tension limits, and compatibility with installation methods such as blowing or pulling. Some cables come with features like low friction jackets to facilitate smooth installation and reduce the risk of damage during the process.
5. Jacket Material:
The jacket material of the optical fiber cable is crucial for protecting the fibers from external elements and ensuring long-term reliability. Common jacket materials include polyethylene (PE), Nylon (PA) polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and low-smoke zero-halogen (LSZH).
Microduct cables need a jacket with low friction to facilitate seamless installation. By using standard lubricants friction can be reduced by more than 50%, and 25% more distance can be reached. The polymer material of the outer jacket should be sufficiently hard yet flexible enough to easily navigate bends and turns. Before cable selection, it is also important to consider the environmental conditions in which the cable will be installed, such as exposure to sunlight, extreme temperatures, or chemical substances, and select a jacket material that provides the necessary protection.
6. General Installation Considerations:
Opt for a fiber optic cable with a low friction coefficient to minimize the air pressure needed for blowing installation. Consider using blowing lubricants for additional friction reduction. Utilize the minimum required pressure for efficient cable pushing through the conduit. Moreover, be mindful of temperature effects; cold temperatures may make the cable jacket brittle, increasing the risk of breakage while air condensation and freezing, can damage the fiber optic cable. The expertise of the installation team is also a crucial factor in the success of the installation process. Ensure tight sealing of connectors in existing ducts to prevent air leakage, reducing pressure drop and enhancing installation efficiency.
Essential Equipment for Fiber Optic Cable
1. Fiber Optic Cable:
The whole blowing process is designed for installing the fiber optic cable, so basically, it’s the most crucial one to carry the information and data transmission.
2. Duct:
The duct in fiber optic installations serves as a protective, organized, and controlled pathway for the fiber optic cable. Simply put, it is a pipe through which the optical fiber cable will be blown. Opt for a smaller diameter duct system for easier fiber optic cable installation compared to larger diameter ducts which is sufficient for today’s range of reduced diameter micro cable.
3. Blowing machine:
Its basic function is to fit the fiber optic cable into the duct by pushing through the provided traction mechanism and facilitating its movement through the conduit or duct by harnessing the drag force generated by compressed air.
4. Air Compressor
An air compressor facilitates the blowing procedure by supplying the air pressure at a constant flow rate to get the fiber optic cable floating through the conduit. Employ an air compressor with a high flow rate to minimize pressure drop during cable installation.

The cost of making the wrong cable selection decision
Selecting the wrong size optical fiber cable for microducts can lead to various issues and costs, both in terms of installation and performance.
Installation and Material Costs:
If the chosen fiber cable is too large for the microduct, it may not fit properly, leading to difficulties in the installation process. Additional labor may be required to modify or replace the microducts to accommodate the larger cable. Moreover, purchasing a larger optical fiber cable than necessary may result in higher material costs.
Performance Issues:
Using a cable that doesn't match the microduct specifications can lead to bending or twisting of the fiber, which can affect signal integrity and result in network performance issues. The wrong size cable may not provide the expected data transmission rates or support future network upgrades.
Downtime and Maintenance Costs:
If performance issues arise due to improper cable sizing, downtime may occur, leading to potential losses in productivity and revenue. Maintenance and troubleshooting costs may increase as technicians need to address issues related to the mismatched cable size.
Long-Term Scalability:
Choosing the wrong cable size may limit the scalability of the network. If future upgrades or expansion plans are hindered, additional costs may be incurred to address these limitations.
Compatibility Issues:
Right cable selection is imperative as incompatible sizes may lead to challenges in connecting with other network components or equipment, requiring additional adapters or connectors, adding to the overall cost.
Regulatory Compliance:
Depending on local regulations and standards, using the wrong cable size may result in non-compliance, potentially leading to fines or legal issues.
To minimize these costs, it's crucial to carefully assess the specifications and requirements of both the microducts and optical fiber cables before making a purchase. Consulting with network engineers, following industry standards, and conducting thorough planning can help avoid these potential pitfalls.
Fiber Optic Cable Blowing Vs Pulling Method
| Feature | Fiber Optic Cables Blowing Method | Fiber Optic Cables Pulling Method |
|---|---|---|
| Damage to Cable | Causes less damage | Potential for more stress and damage during the pulling process |
| Likelihood of Getting Stuck | Less likely to get stuck | Higher chance of cable snagging or getting stuck in the conduit |
| Speed of Installation | Faster than any other method | Slower, requires more time and manpower |
| Suitability for Long Conduits | Suitable for long conduits even up to 2km | Not Suitable for long conduits |
| Installation around Bends | Suitable for bends and obstructions | Requires careful planning for bends and obstructions |
| Requirement for Manpower | Need labor at one end to start the installation | Need labor at both ends to start the installation |
How to choose the right microcable for a microduct?
Surprisingly there is a tool that can help you make the right microduct cable selection. This tool is “Microduct Blown Cable Advisor Tool” from HFCL Ltd. a leading technology company specializing in creating digital networks such as 5G, Optical Fiber and Cables, Wi-Fi, etc. for telcos, enterprises, and governments. It is a valuable resource for those seeking to make informed decisions in the realm of cable selection.
The tool offers the following benefits to network operators:
Intelligent Cable Recommendations: The microduct blown cable advisor tool stands out for its ability to provide tailored cable recommendations based on specific network requirements. By factoring in variables such as duct diameter, fiber count, and cable type, users can gain insights into the most suitable options.
Cost Savings and Efficiency: Beyond mere cable recommendations, the tool serves as an efficiency booster by streamlining the cable selection process. This, in turn, translates to time savings and a reduction in manual processes. Notably, the tool emphasizes the elimination of unnecessary maintenance, aligning cable choices with the network's specific needs to achieve long-term cost savings.
Being Future-Ready: This microduct cable selection tool encourages users to adopt a forward-looking perspective by considering evolving network requirements and technological advancements. Users can select blown cables that not only meet current demands but also allow for future upgrades and scalability. This foresighted approach is integral for maintaining a competitive edge in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
This tool is designed to assist users in comprehending cable design and assessing installation performance. By leveraging this resource, network operators can enhance their knowledge, make informed choices, and align their networks with the demands of the digital future.
Conclusion:
The best microduct cable selection involves thoughtful consideration of various parameters to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. By carefully evaluating factors such as fiber count, cable construction, jacket material, microduct size, and installation considerations, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your network's current and future requirements. Investing time in selecting the right microduct cable is a crucial step toward building a robust and future-proof fiber optic infrastructure.