Every passing day brings an escalation in the number, variety, and intensity of threats faced by both military and civilian assets. The battlefield is ever-evolving, with adversaries becoming increasingly sophisticated and their tactics more insidious. In such a challenging landscape, the need for dependable surveillance becomes paramount to safeguard critical missions and protect armed forces deployed in theatres of operation worldwide.
Ground Surveillance Radar (GSR) is a vital product in detecting, tracking, and monitoring the movements within a certain range in infrastructures such as military camps, airfields, country borders and commercial airports. These advanced systems possess the capability to detect even the slightest ground-level movements with precision. Ground surveillance Radars play a pivotal role in national security by identifying and tracking small, evasive, and non-cooperative targets. They offer a wide operational range, spanning from several hundred meters to over 10 kilometres.
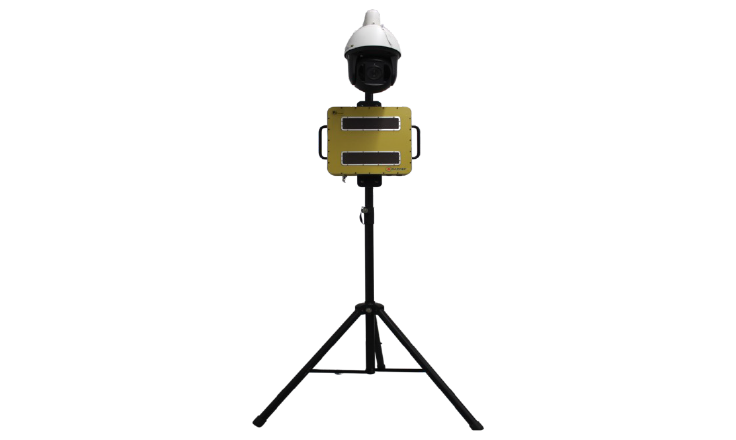

What is Ground Surveillance Radar?
Ground Surveillance Radar Systems are completely indigenous, making them highly reliable and technologically advanced. These radars are built on Frequency-Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) technology, and we incorporate cutting-edge electronic scanning (e-scan) antennas, ensuring superior performance and accuracy. These radar systems are engineered to endure severe weather conditions without experiencing any mechanical deterioration.
Despite their capabilities, these radars maintain a lightweight and compact design, making them easily portable and quickly deployable. These systems operate efficiently 24/7, supported by a battery as a backup power source, providing uninterrupted surveillance even in challenging environments.
The versatility of these radars allows them to detect various targets, including humans in different movements like strolling and sprinting, compact and oversized ground vehicles, drones at low altitudes, and aerial vehicles, as well as boats.
The cost-effective solution can be ideal for perimeter surveillance across a range of locations, such as international borders, coastlines, tall buildings, airports, prisons, and industrial sites. By efficiently checking and monitoring intrusions, these radars enhance security measures and contribute to ensuring the safety of critical assets and installations.
Different Types of Ground Surveillance Radar
Very Short Range Radar:
Very Short Range Radar (VSR) is based on state of-the-art FMCW technology with latest generation e-scan antennas which works in Ku band with detection range of 1.5 kms and can track upto 100 targets simultaneously

Short Range Radar:
Short Range Radar (SR) is based on state of-the-art FMCW technology with latest generation e-scan antennas which works in Ku band with detection range of 11 kms and can track upto 300 targets simultaneously.
Medium Range Radar:
Medium Range Radar (MR) is based on state of-the-art FMCW technology with latest generation e-scan antennas which works in Ku band with detection range of 30 km and can track upto 700 targets.
Unique Features of Ground Surveillance Radar
The Ground Surveillance Radar Systems are characterized by their lightweight, compact size, and rapidly deployable. These advanced radars are designed to meet the diverse needs of security and surveillance in critical areas. The radars' light-weight nature ensures easy mobility, enabling quick transportation and swift deployment in various scenarios. Their compact size allows for seamless integration into constrained spaces, making them self-effacing yet highly efficient in their surveillance capabilities.
A standout feature of these radars is their remarkable ability to detect crawling and moving persons, making them ideal for security operations in areas where stealth and precision are crucial. Additionally, their cutting-edge technology enables accurate detection of both light and heavy vehicles, offering comprehensive surveillance coverage.
Key Advantages of Ground Surveillance Radar
The integration of Ground Surveillance Radar (GSR) has proven to be a valuable addition to perimeter intrusion detection and assessment systems. GSRs offer three remarkable enhancements that boost their effectiveness:
- The ability to operate in challenging visibility conditions,
- Precise ranging and tracking capabilities, and
- Seamless integration with modern video systems for both assessment and surveillance purposes.
One of the standout features of GSRs is their ability to detect and track targets over long distances, extending several kilometres, while simultaneously providing a wide 360° field-of-view (FOV). This extensive coverage ensures that targets of various sizes and speeds are effectively monitored, significantly enhancing the overall capabilities when combined with conventional perimeter intrusion detection systems.
The integrated system operates by using an adaptive threshold to identify any motion of objects that deviate from the established background. Once detected, the objects are continuously tracked across range to ascertain their current and predicted paths. If the path encroaches into a designated area, the system raises an alarm to prompt immediate action.
What are the Applications of Ground Surveillance Radar?
Ground Surveillance Radar has a wide range of applications in various industries due to its ability to detect and track objects on the ground accurately. Some of the key application areas include:
National Boarder Security: Ground Surveillance radar systems play a vital role in monitoring and securing national borders. They assist border patrols in detecting illegal crossings, smuggling activities, and suspicious movements along the borders.
Perimeter Security: Ground Surveillance Radar can be used in different places like Industrial facilities, corporate campuses, and private estates to enhance perimeter security by detecting any unauthorized intrusions or trespassing.
Airport Security: Ground Surveillance Radar is an indispensable technology that plays a vital role in maintaining safe ground operations at airports and airfields, safeguarding both personnel and valuable aircraft assets. Its integration with air traffic management systems ensures seamless coordination between air and ground operations, supporting the smooth functioning of the aviation industry.
Wide Area Surveillance: GSR is also used for wildlife monitoring and conservation purposes. It helps track animal movements, especially in remote areas, assisting researchers and environmentalists in studying wildlife behaviour and population patterns.
Coastline Security: Ground Surveillance Radar systems find application in maritime security by facilitating the monitoring of maritime traffic and detecting suspicious activities, including illegal fishing and smuggling.
Final Words:
The global demand for Ground Surveillance Radar systems is on the rise due to its ability to replace multiple non-specialized Radar systems. Its versatile capabilities allow for the detection of land vehicles, personnel, marine vessels, avian targets, and low-flying aircraft, making it an ideal choice for accurate and comprehensive surveillance.
Furthermore, Ground Surveillance Radar systems are increasingly used for tracking and detecting aircraft at low altitudes, making them indispensable for security and monitoring purposes. With such key features and capabilities, the global Ground Surveillance Radar market is expected to witness substantial growth as organizations recognize the value and efficiency these systems bring to various applications and industries.