Fiber-To-The-Home (FTTH) technology is revolutionizing the way people access the internet, and it is becoming increasingly popular across Europe, especially in Germany. In this blog, we'll explore the benefits and challenges of FTTH Germany and Europe and look at how it is changing the way people connect to the internet. Keep reading to know more!
Fiber to the Home (FTTH) is a technology that uses fiber optic cables to deliver internet directly to homes. In Europe, this technology is gaining traction, as fiber cable allows for higher speeds and greater reliability than older technologies like copper wire. FTTH solutions typically include fiber-optic cabling from a fiber node directly to the subscriber’s home or business premises, creating a stronger FTTH network and future-ready digital infrastructure.
The fiber connection has many advantages: -
- a. It enables much faster download and upload speeds (speed of FTTH) than traditional copper wiring.
- b. It allows smoother video streaming, gaming, and browsing the internet.
FTTH Coverage in Germany
A total of 198 million (M) homes in Europe can currently access FTTH/B services. According to the most recent study, which was commissioned by the FTTH Council Europe, that number is expected to increase by more than 50% over the course of the following five years, reaching more than 300 million houses.
Even though Germany is very strong in broadband with about 95 percent coverage, its fiber coverage is far behind with fiber to the home (FTTH) coverage at only 10.5%. Additionally, due to the shared nature of the technology, most broadband is accessed using xDSL or DOCSIS technology at substantially lower speeds than stated.
Consumer adoption is low even when fiber is available, with a Germany FTTH market take-up of less than 30% in the build-out areas. Moreover, enterprises that link business parks with fiber could struggle to achieve significant consumers as sometimes the penetration is as low as 10%. While the technology is widely available in urban areas, it is still relatively scarce in rural areas, where residents often have to rely on slower broadband options, with coverage reaching only 2.4 percent of rural households. The digital divide is a major concern, as it means that certain parts of the country are being left behind in terms of connectivity.
To address this situation, government in Germany has taken several measures. Government incentives to switch to full- fiber networks have been increased, which has aggravated the desire and accelerated adoption. A countrywide expansion of gigabit networks by 2025 was included in the coalition agreement of the German Federal Government, along with a strategy to build out fiber infrastructure in local businesses and educational institutions across the country. With funding commitments of up to €30 million, the German government plans to promote rural FTTH projects. The German funding plan also specifies a particular material concept that requires for a minimum of 10/6mm microducts to connect households.
Additionally, operators like Deutsche Telekom continue to expand optical networks, contributing to wider access networks and improving fiber optic connections across the country.
FTTH Forecast for Germany
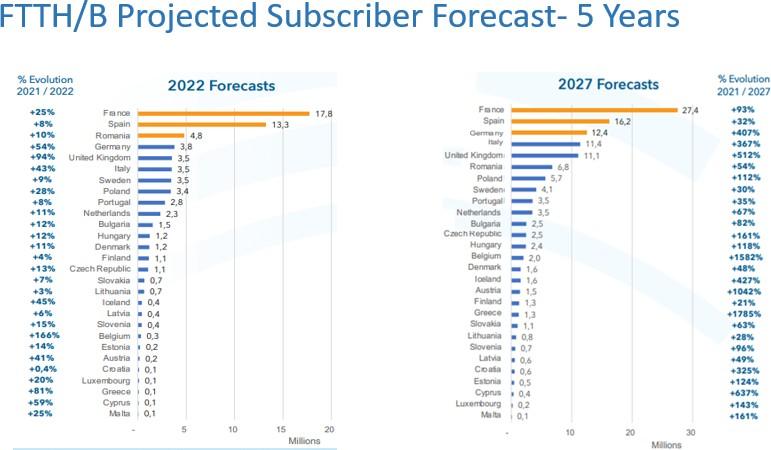
Currently, only 9.1 million of the 40 million households that the German government has ordered be connected to FTTH are now serviced, leaving a market opportunity of 31 million households. Germany's fiber market is expected to increase by 407% to 12.4 million by 2027 from its current level of 2.4 million by that time.
Having such a huge opportunity, HFCL have started discussions with major operators on linking 15 million homes. With one of the main telecom companies in Germany, HFCL is about to successfully complete its POC of 400 households.
Having such a huge opportunity, HFCL has started discussions with major operators on linking 15 million homes. With one of the main telecom companies in Germany, HFCL is about to successfully complete its POC of 400 households, contributing to the accelerating Germany FTTH rollout.
Benefit of Fiber to home (FTTH) Rollout in Germany
To sum up, FTTH rollout in Germany unquestionably offers an alluring opportunity for both foreign investors and businesses. Once the target is achieved, it will change the outlook of Germany not only in Europe but across the globe. With fiber optic internet, users will have access to secure encryption protocols that protect their data from unauthorized access. Consequently, fiber optic internet will provide users with an unparalleled level of security without sacrificing speed or reliability.
It will also allow for more people to access the internet simultaneously, so households can stay connected without experiencing any slowdowns in speed and connectivity. Home FTTH brings higher capacity directly to users, eliminating shared bandwidth and interference.
FTTH will provide fiber optic cables directly to the home, rather than terminating the connection at a nearby node. This will allow for greater bandwidth and speeds up to 10 Gbps, with no shared resources and less interference between connections. Fibre optics and optical fiber technology will continue to revolutionize modern communication and help reduce the digital divide
FAQs
FTTH stands for "Fiber to the Home," and it is a type of broadband internet service that delivers high-speed internet through a fiber optic network.
In an FTTH network, fiber optic cables are laid directly to individual homes or buildings, instead of terminating at a distribution box or cabinet. This means that the fiber optic cables carry the data all the way to the end-user's premises, providing faster and more reliable internet connectivity.
Compared to traditional internet services that rely on copper cables or coaxial cables, FTTH fiber offers much higher bandwidth, which enables faster downloads and uploads, and lower latency. It also supports high-quality streaming of video and audio content, making it a preferred choice for applications like video conferencing, online gaming, and media streaming.
Fiber and copper cables are both used to transmit data, but they have some significant differences.
Speed and Bandwidth: One of the main differences between fiber and copper cable is the speed and bandwidth they provide. Fiber optic cables can provide much higher bandwidth and faster data transfer rates than copper cables. This is because fiber cables use light to transmit data, which travels much faster than electricity in copper cables.
Distance: Another difference is the distance over which they can transmit data without losing quality. Copper cables can transmit data up to 100 meters before the signal starts to degrade, whereas fiber optic cables can transmit data for much longer distances without any loss in quality. This makes fiber optic cables ideal for long-distance communications.
Interference: Copper cables are susceptible to electromagnetic interference from other electrical devices, which can cause signal degradation and data loss. In contrast, fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, making them more reliable in noisy environments.
Security: Fiber optic cables are more secure than copper cables, as they are difficult to tap without being detected. Copper cables can be easily tapped, allowing someone to intercept data without detection.
Cost: Fiber optic cables are generally more expensive than copper cables, but they offer many advantages in terms of speed, bandwidth, distance, and security. Over the long term, fiber optic cables can be more cost-effective due to their low maintenance requirements and long lifespan.
The maximum speed of FTTH (Fiber to the Home) can vary depending on several factors, such as the service provider, the quality and capacity of the fiber optic network, the type of equipment used, and the package subscribed to by the customer. However, generally, FTTH can provide much higher speeds than traditional internet services that use copper or coaxial cables.
In some areas, FTTH can provide symmetrical speeds, which means that the download and upload speeds are the same. Some service providers offer FTTH packages with download speeds of up to 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps), while others may offer even faster speeds of up to 10 Gbps.
The actual speed that a customer can achieve will depend on several factors, such as the quality of the customer's equipment, the number of devices connected to the network, and the network congestion. Additionally, the speed may also vary based on the time of day and the geographic location of the customer.













Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.