"Why would seaports require 5G?" This is undoubtedly the question on the minds of many in the industry, accustomed to the traditional methods of trade. To grasp the significance of 5G in ports, we must recognize that the maritime industry is not solely about moving goods from one place to another. Instead, it plays a vital role in international trade and economic growth. You would be surprised to know that the main transport mode for global trade is ocean shipping. Yes, around 90% of traded goods are carried over waves. Therefore, it is evident that beyond the surface of loading and unloading cargo, seaports are essential hubs that connect nations and shape markets worldwide.
While traditional seaport businesses thrived without advanced technology like 5G in the past, the present day demands a whole new level of innovation and efficiency. Today's seaports confront an ever-evolving, fiercely competitive global landscape, presenting them with fresh challenges to overcome.
Challenges in the Maritime Industry
Dock to Door: Inefficient Cargo Handling
The maritime industry has long grappled with the challenge of inefficient cargo handling. The port industry operates relentlessly, requiring non-stop, round-the-clock services year-round. Renting large vessels incurs significant costs, billed daily, leaving no room for delays or prolonged operations that result in financial losses and dissatisfied customers. The use of wireless communications in container yards and quayside container crane areas, primarily enabling remote control of vertical transportation and unmanned driving of horizontal transportation means can help overcome this challenge. However, despite these advancements, controlling vertical transportation means, like gantry cranes, and unmanned driving of horizontal transportation means, such as Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), remains complex. Traditional operator cabins atop crane present safety risks and limited visibility, hindering optimal performance.
Traffic Tsunami: Difficulty Managing Maritime Traffic
One of the primary challenges in the maritime industry is the sheer volume of ships entering and leaving busy ports. As global trade continues to thrive, the number of vessels plying the waters has surged exponentially, putting immense pressure on maritime traffic management systems. Without robust coordination and real-time communication, ships often find themselves caught in long queues, waiting for berths to become available. As waiting times increase, so does the wastage of fuel, resulting in unnecessary costs and a larger carbon footprint. Additionally, the lack of seamless data exchange and communication between vessels and port authorities compounds the challenge. Ship captains struggle to access real-time updates on docking availability, making it difficult to plan efficiently.
Navigating Stormy Waters: Adverse Weather Conditions
Unpredictable adverse weather conditions, such as storms and high winds, can force ships to seek shelter, alter routes, and delay schedules. These disruptions lead to increased operational costs, inefficiencies in cargo handling, and frustrated customers. Weather-related uncertainties make it difficult for operators to plan and execute maritime operations effectively. Without access to real-time weather data and swift decision-making capabilities, operators are left ill-equipped to adapt promptly to changing conditions. As a result, cargo schedules fluctuate erratically, impacting the overall supply chain and causing financial losses for both the industry and its customers.
Heed the Sea: Danger May Lie Beneath
Worker safety is another major challenge in the maritime industry. The diverse nature of port activities exposes workers to an array of potential hazards. With heavy cargo, dangerous equipment, and various other hazards present, port workers face daily risks of injury. Alarming 2018 data from the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) reveals that nearly 42% of marine casualties or incidents occurred in port areas, underscoring the urgency of addressing safety concerns. Moreover, workers often encounter changing environmental conditions, ranging from adverse weather events to slippery surfaces, amplifying the complexity of ensuring their safety.
Lost at Sea: Communication Challenges
Imagine a bustling seaport, handling countless vessels and containers every day. Traditionally, communication within such a dynamic environment relied on wired connections, limiting mobility and efficiency. However, as smart ports evolve, the demand for advanced communication systems becomes critical. These systems must support low latency, high bandwidth, and reliable communication services to handle the control data and multi-channel video data of port equipment. Legacy communication methods based on optical fiber and Wi-Fi often incur substantial deployment and maintenance costs. Moreover, their performance in handling such critical data can be suboptimal, characterized by poor stability and low reliability.
Phishing at Ports: Battling Data Security Threats
As the maritime industry embraces the digital age, data security becomes one of the major challenges of the maritime industry. Traditionally, the maritime sector was deemed relatively safe from cyber threats due to the lack of widespread internet connectivity and the isolated nature of ships at sea. However, recent developments have brought forth a pressing challenge: a staggering 900% increase in cybersecurity breaches targeting operational technology in the maritime sector. This exponential rise in cybersecurity breaches is particularly alarming, as it poses significant risks to maritime operations, safety, and the overall supply chain. Operational technology refers to the systems and devices that control critical processes, such as navigation, communication, cargo management, and engine control. Cyberattacks targeting these systems can lead to disruptions in vessel operations, data theft, financial losses, and even pose risks to crew safety and the marine environment.
5G in Ports: Addressing Maritime Industry Challenges
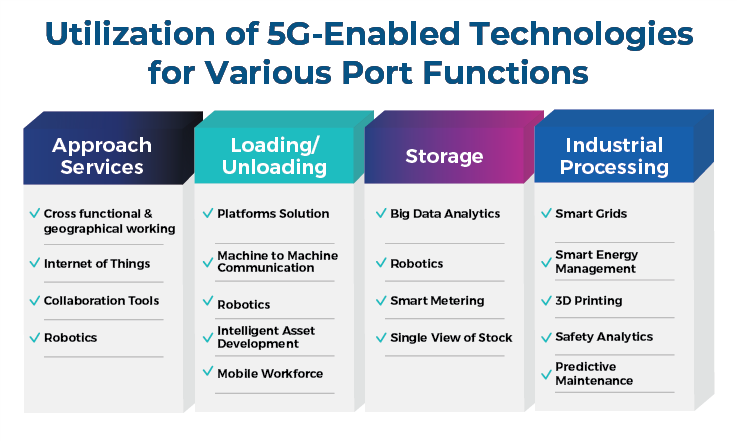
Taking Charge: Remote Controlling
Now, we are not talking about some video games or robotic cars, we are talking about remote control of vertical transportation means, such as gantry cranes, and unmanned driving of horizontal transportation means, such as Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs). The successful implementation of remote control relies heavily on high-speed and reliable network connectivity. Only 5G can provide the necessary uplink bandwidth of 100 Mbps or more, ensuring smooth video uploads and reliable PLC communications. This allows one operator to efficiently control 3 to 6 gantry cranes simultaneously, significantly improving port operations.
Casting the Net: Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in transforming ports into smart and efficient hubs. Machine vision, a subset of AI, empowers computers to recognize patterns and objects in video feeds. In port environments, machine vision enables automatic monitoring of berths, personnel, and traffic flow. The implementation of 5G in ports is pivotal in this context. The technology enables seamless connectivity of thousands of cameras and sensors to a single network, facilitating real-time data processing through Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC). This significantly reduces the cost of the machine vision system and enhances its efficiency. Various AI applications have been deployed in ports, including the identification of container IDs using crane cameras, intelligent analysis of an operator's facial expressions for fatigue and drowsiness detection, and license plate and cargo recognition for efficient operation management.
Smart Ports and Smart Ships
Smart ports leverage vast amounts of data to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making. Connected ships play a critical role in the smart port ecosystem by gathering real-time water, weather, and communications data. This data is analyzed to provide valuable insights to ship and port operators, enabling better navigation and communication. The use of 5G's Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC) and Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC) ensures improved security and safety during ship navigation. Cameras onboard ships communicate in real-time with the port, allowing for remote assistance and monitoring of ship movement. The incorporation of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) aids in further enhancing crew safety and operational efficiency.

Smooth Operations: Efficient Cargo Handling
5G-powered Internet of Things (IoT) devices on gantry cranes enable remote and automated cargo handling throughout the port. These devices collect and transmit real-time data, such as time, trip distance, routes followed, and cargo weight, to the port management. This real-time data allows for optimized ship-to-shore operations, reducing handling time per cargo unit, and minimizing operational inefficiencies.
Kalmar, a leading crane manufacturer, highlights that the implementation of remote-controlled cranes could potentially release up to 70% of operators to perform other tasks during periods of low activity when ship loading and unloading demands are reduced.
Waves of Automation: AGVs, Drones, and Autonomous Trucks
Based on information obtained from the International Maritime Information website, roughly 75% of port operators consider automation to be a critical factor in maintaining competitiveness over the next three to five years. Leading this transformation are Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), essential assets in port logistics, autonomously handling cargo operations with the support of 5G technology. Drones contribute valuable topographic information for port planning, despite certain limitations. Furthermore, self-driving trucks hold promise for the future of port operations, collecting real-time data to navigate autonomously. With 5G's network slicing ensuring safety, automation promises unmatched efficiency, safety, and global port competitiveness, driven by the transformative potential of 5G in ports.
Strengthening the Safety Net: 5G for Cybersecurity
5G technology offers significant advantages in strengthening data security at seaports. With advanced encryption algorithms and built-in security features, 5G in ports ensures highly protected data transmission, safeguarding against potential cyber threats and unauthorized access. Its low latency facilitates real-time data processing, enabling quicker detection and response to security incidents. Network slicing allows the creation of dedicated, secure communication channels for critical applications. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, preventing security threats to sensitive information. Furthermore, 5G enables the creation of secure private networks tailored to specific security needs, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Benefits of Using 5G in Ports:

Final Words:
As more ports around the world embrace 5G technology, the benefits will ripple across the entire supply chain, creating a more efficient, safer, and environmentally responsible global trade ecosystem. In the future, the development of smart ports will be crucial to the port industry, driven by trends like device automation, intelligent scheduling, and data visualization. 5G in ports will enhance port operations and offer real-time data insights and resilience. This transition to smart ports will propel the industry towards a more connected, efficient, and sustainable future, embracing the dynamic landscape of Ports 4.0. Collaboration and adaptability will be vital as we navigate the waves of innovation, shaping the future of the global maritime industry for generations to come.